Our previous series of articles has covered the basics of press brake dies in detail. We wrote those articles to introduce you to the types and names of press brake dies. If you’re no longer satisfied with just acquiring this primary knowledge, we’ve got you covered with more in-depth content.
In this article, we will provide advanced knowledge about press brake dies. These include the materials used for press brake dies and the manufacturing technique of brake press dies. We believe that the following content will definitely answer your related doubts. Let’s get started!

What are Press Brake Dies?
Sabemos que es posible que no haya leído la serie de artículos que escribimos sobre matrices de plegadoras. Así que aquí estamos nuevamente con una breve descripción general de qué son las matrices de plegadoras. También puedes leer ambos artículos directamente.
Los tipos de herramientas de plegadora (punzones de plegadora)
Una guía para matrices de plegadoras (punzones y matrices)
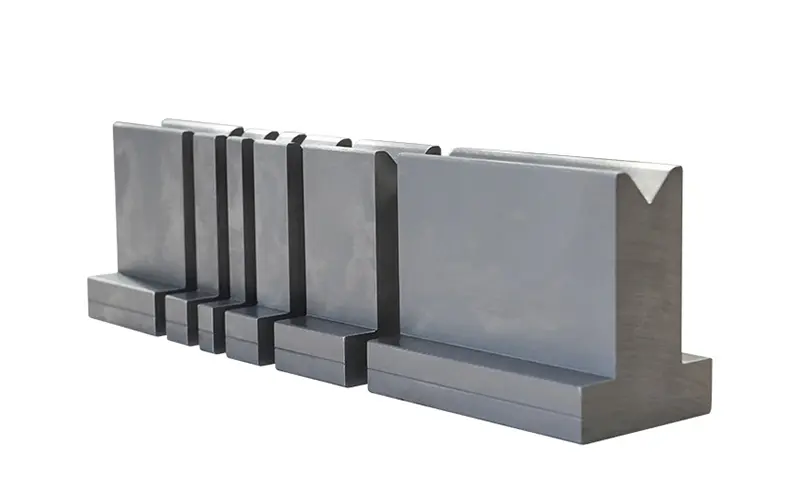
En el proceso de plegado de chapa, los fabricantes utilizan una máquina plegadora. Los troqueles de la plegadora están en contacto directo con la chapa. La máquina plegadora aplica fuerza a la chapa a través de troqueles para doblarla. Los troqueles de prensa plegadora se componen de dos partes centrales y otras partes auxiliares. Estas dos partes centrales son el troquel superior y el troquel inferior. Algunas personas se refieren a estas dos partes como golpear y morir.
As you can see in the picture below, the two blue parts are the upper die and the lower die. The lower die is stationary, and the upper die can move up and down under the control of the machine. With the cooperation of the upper die and the lower die, the operator can bend the sheet metal into the desired shape.
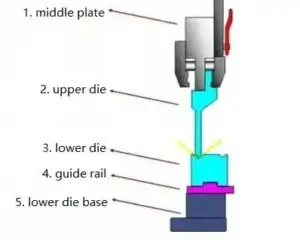
Otras piezas auxiliares son útiles para que el troquel superior y el troquel inferior realicen sus tareas. Su tarea más importante es mantener el troquel superior y el troquel inferior en una posición estable. Esto se debe a que es un factor importante que afecta la flexión de la chapa. En este contexto, las piezas auxiliares también garantizan que el operador tenga la flexibilidad de cambiar el troquel superior y el troquel inferior.
Manufacturing process of the press brake
1. Press brake dies materials
Press brake dies made from different materials have different indicators for different uses. Currently, press brake manufacturers mainly use steel as the basic material for press brakes. Alloys formed by adding other elements to steel are also common for press brake dies. In addition to these, press brake dies made from polymers also have a wide range of applications.
-
T8A and T10A carbon tool steels
T8A and T10A are two common types of Carbon Tool Steel. Both steels typically contain between 0.7% and 1% carbon. In addition, steel manufacturers can further enhance the hardness of these two steels through heat treatment. So if high hardness press brake dies are required, dies made with this steel are the first choice. Dies made with higher hardness materials can bend harder sheet metal.
Además de esto, el acero para herramientas al carbono es muy resistente al desgaste. Esta propiedad proporciona a las prensas plegadoras una vida útil más larga y reduce los costos de producción. Pero el acero para herramientas al carbono tiene sus desventajas. Debido a la dureza asociada con el alto contenido de carbono, los aceros para herramientas al carbono son generalmente relativamente frágiles. Esta característica da como resultado que los troqueles de plegadoras fabricados con este material sean frágiles ante las fuerzas de torsión.

-
Low-alloy tool steel
Para mejorar las deficiencias del acero para herramientas al carbono, la adición de pequeñas cantidades de elementos de aleación puede mejorar eficazmente su tenacidad. Los troqueles de las plegadoras fabricados con acero para herramientas de baja aleación pueden proporcionar una mejor resistencia a la fractura cuando se someten a fuerzas de impacto o torsión.
-
High carbon and high chromium / medium chromium tool steel
This material can be produced by adding a certain amount of chromium to high-carbon tool steel. As you can literally see, the level of chromium content is the key to differentiating between the two materials. High carbon and high chromium tool steels typically contain more than 12% chromium. High carbon and medium chromium tool steel generally contains between 4% and 12% chromium. However, the production of this material is difficult. A special process is required to achieve a uniform distribution of carbon during the production of this material.
In order to improve this problem, the content of chromium has been reduced to produce high-carbon and medium-chromium tool steel, which has better properties and less distortion when subjected to heat treatment.
-
High-speed steel
High Speed Steel (HSS) is a specialty tool steel. HSS has a high hardness and can be heat-treated (e.g., hardening and quenching) to obtain higher hardness levels. Due to the addition of alloying elements (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, etc.), HSS typically exhibit good wear resistance. This enables them to maintain a long service life during prolonged cutting operations.
Due to the addition of alloying elements, HSS typically exhibits good heat resistance. This allows them to maintain their hardness and durability at high temperatures. When making press brake (bending machine) molds, the high hardness of HSS provides better wear resistance and cutting results. Heat resistance is the most outstanding feature of HSS. In a high-temperature environment, a press brake die made with HSS can also maintain better performance.
-
Basic steel
El acero básico se crea incorporando pequeñas cantidades de elementos adicionales y ajustando el contenido de carbono. Este proceso conduce a mejoras notables en sus características en comparación con el acero rápido. Las mejoras en el acero básico para aplicaciones de matrices de plegadoras dan como resultado una mayor resistencia al desgaste y dureza, junto con una mayor resistencia a la fatiga y tenacidad.
Como resultado, el acero básico es una excelente opción para el acero de matrices de plegadoras, ya que ofrece resistencia y tenacidad excepcionales. Además, proporciona una alternativa más rentable al acero rápido.
-
Cemented carbide and steel-bonded cemented carbide
Cemented carbide exhibits the highest hardness and wear resistance among press brake die steels. However, its strength and toughness during bending operations are relatively poor. Tungsten and cobalt are commonly used materials for cemented carbide in press brake dies. When low impact and high wear resistance are required, cemented carbide with a low cobalt content is preferred.
Conversely, for high-impact dies, cemented carbide with a high cobalt content is utilized. Steel-bonded cemented carbide is produced through powder metallurgy techniques. It involves using iron powder as the binder along with a small amount of alloy element powder, such as chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, or vanadium.
Este material puede sufrir procesos de corte, soldadura, forja y tratamiento térmico. Después de someterse a procesos de enfriamiento y revenido, la dureza del carburo cementado aglomerado con acero puede alcanzar un rango de 68-73 HRC.
-
New materials
Manufacturers are now starting to use new materials when making press brakes. The most commonly used new material is cold-working die steel. This material has excellent abrasion resistance and is well-suited for press brake dies. There are two methods that could improve these new materials. And both methods focus on HIGH ALLOY STEEL D2 (Cr12MoV).
The first direction aims to enhance the toughness of press brake dies. Reducing the carbon and alloy element content can improve the uniform distribution of carbides within the steel. Examples of the first approach, aimed at enhancing the toughness of press brake dies, include 8CrMo2V2Si and Cr8Mo2SiV. These materials are designed to reduce the carbon and alloy element content. It can also improve the uniform distribution of carbides within the steel.
La segunda dirección en el desarrollo del acero para troqueles para plegadoras se centra en mejorar la resistencia al desgaste. Esto implica desarrollar materiales que puedan soportar las exigentes condiciones de tales operaciones. Esto se logra mediante el uso de acero en polvo de alta velocidad. Un ejemplo en esta categoría es 320CrVMo13.

2. Tratamiento térmico
Por supuesto, es importante elegir el material adecuado para fabricar la prensa plegadora. Sin embargo, también es necesario procesar el material utilizando la tecnología de procesamiento correcta. El tratamiento térmico de piezas metálicas puede aumentar significativamente sus propiedades. Hay dos tipos comunes de tratamiento térmico:
Quenching
El enfriamiento es un método común de tratamiento térmico. Durante la producción de plegadoras, los fabricantes utilizan el enfriamiento para eliminar las tensiones internas del material. Los pasos principales de este método constan de los siguientes componentes.
First, the steel is heated at a high temperature. When the temperature of the metal material exceeds a certain limit, its structure changes. Then the material needs to be cooled at a certain rate. Different cooling rates will result in different material properties. For example, if the hardness of the material needs to be increased, the cooling rate needs to be increased. If the material needs to be made tougher, it needs to be cooled more slowly.

Hardening
El enfriamiento y el endurecimiento son dos pasos relacionados pero distintos en el proceso de tratamiento térmico. El endurecimiento es el proceso de aumentar la dureza y resistencia de un material metálico. Además del temple, existen otros métodos para lograr el endurecimiento, como el tratamiento con solución sólida y el envejecimiento.
During the hardening process, the metallic material usually undergoes steps such as heating, holding, and cooling. These steps can change its crystal structure and increase its hardness.
Induction Hardening And Core Hardening
El endurecimiento por inducción y el endurecimiento del núcleo son dos tratamientos térmicos relacionados pero diferentes. Ambos métodos endurecen solo una parte de los troqueles de la plegadora. El primero trata sólo la superficie de las matrices del freno de presión. Este último se ocupa únicamente del interior. El endurecimiento por inducción puede fortalecer en gran medida la dureza de la superficie de las matrices de frenos de presión. El endurecimiento del núcleo proporciona una resistencia constante a todas las partes de los troqueles de la plegadora. Sin embargo, este proceso hace que la superficie de los troqueles de la plegadora se desgaste más fácilmente.








